See all blog posts in this series:
- OpenShift Virtualization on IBM Cloud, part 1: Introduction
- OpenShift Virtualization on IBM Cloud, part 2: Becoming familiar with VPC
- OpenShift Virtualization on IBM Cloud, part 3: Deploying ROKS, ODF, and OCP Virt
- OpenShift Virtualization on IBM Cloud, part 4: Creating a virtual machine
- OpenShift Virtualization on IBM Cloud, part 5: Migrating a virtual machine
- OpenShift Virtualization on IBM Cloud, part 6: Backup and restore
- OpenShift Virtualization on IBM Cloud, part 7: Dynamic resource scheduling
For KubeVirt virtual machines, it’s possible to use pod affinity specifications to designate both affinity and anti-affinity rules for your virtual machines.
However, you have to take some extra steps to enable dyanamic resource scheduling (what in the VMware world is called DRS—distributed resource scheduler). After following these steps, the system will periodically rebalance your virtual machines, taking into account any affinity and anti-affinity rules as it does so.
Install and configure Descheduler
First you must install the descheduler tool which performs the dynamic scheduling. RedHat provides a supported form of this using their Kube Descheduler operator, which is available in your cluster in the OperatorHub.

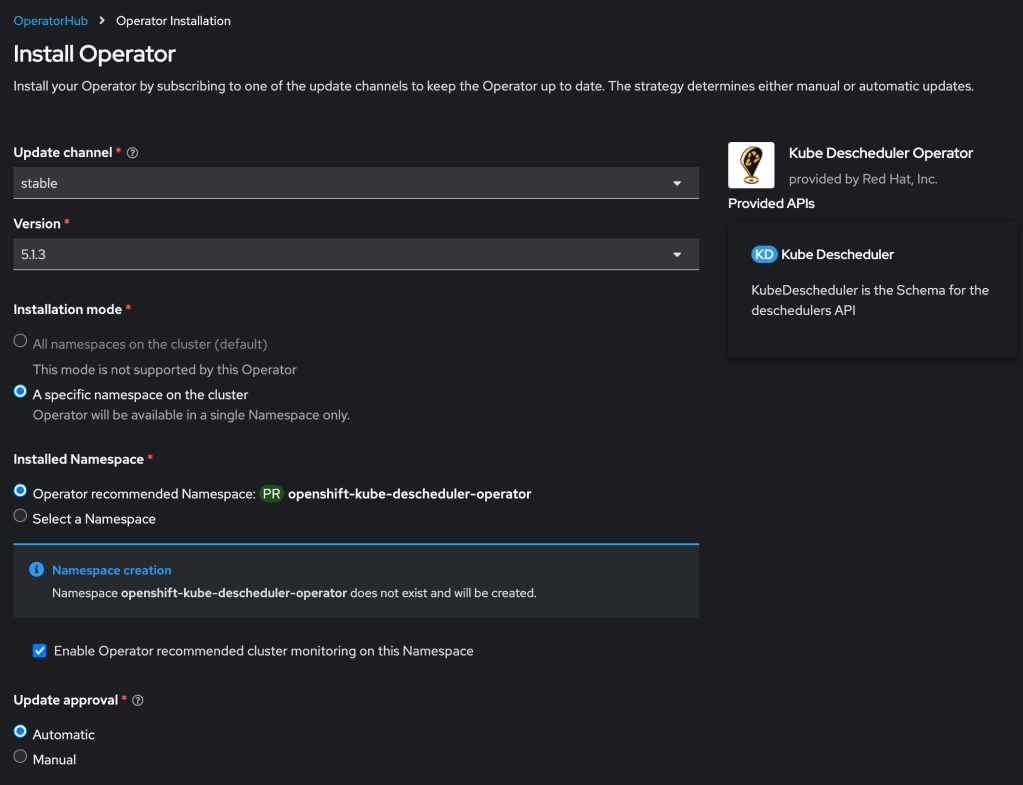
Then you need to create a KubeDescheduler resource describing your rescheduling plan:
Working with the RedHat KubeDescheduler documentation and some failed attempts at experimentation, I crafted the following example definition. Note that currently this leverages two dev keywords that will be folded into the product formally over time.
kind: KubeDescheduler
apiVersion: operator.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: cluster
namespace: openshift-kube-descheduler-operator
spec:
deschedulingIntervalSeconds: 300
managementState: Managed
mode: Automatic
profiles:
- AffinityAndTaints
- DevKubeVirtRelieveAndMigrate
- EvictPodsWithPVC
- EvictPodsWithLocalStorage
profileCustomizations:
devEnableEvictionsInBackground: true